In this blog, we will explore the main storage options in GCP and identify their use cases.
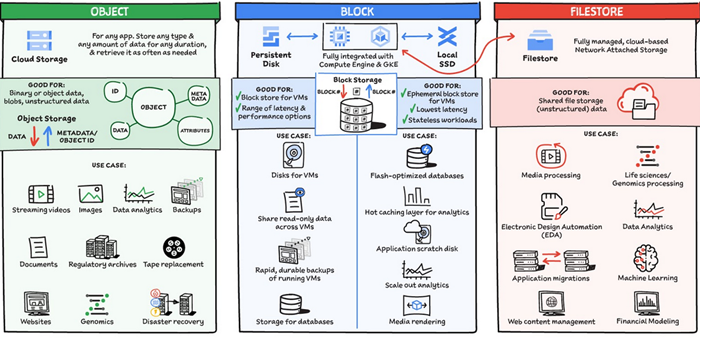
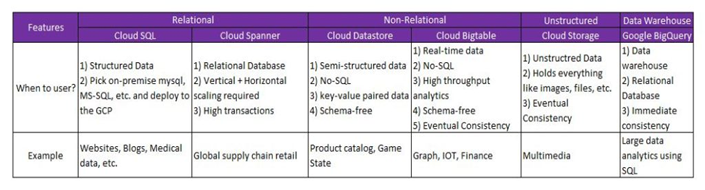
We will explore these storage and database options only: Cloud Storage, Cloud SQL, Cloud Spanner, Cloud Datastore, and Cloud Bigtable. Based on data types, it has three store categories: Object, Block, and Filestore. The graph below indicates their use cases and advantages.
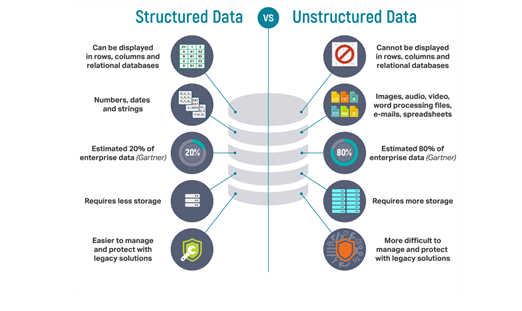
What is more, there are two types of data: Structured and Unstructured; we are going to encounter. Thus, different types of data would be stored in different storage platforms.
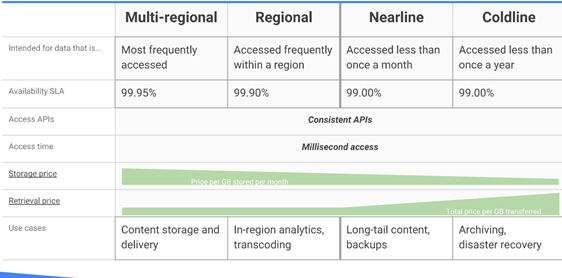
Cloud Storage is an object store for binary and object data, blobs, and unstructured data. 4 storage classes are based on budget, availability, and access frequency:
Cloud SQL is a fully managed service that makes it easy to set up, manage, and manage relational databases.
Cloud Bigtable is a compressed, high-performance, and highly scalable data storage system based on the google file system. It is used to store large-scale structured data suitable for cloud computing.
Cloud Spanner is a global distributed relational database management system developed by Google inc. It is the successor of BigTable.
Cloud Datastore is a seamless datastore in GCP.
Where should your application store data?
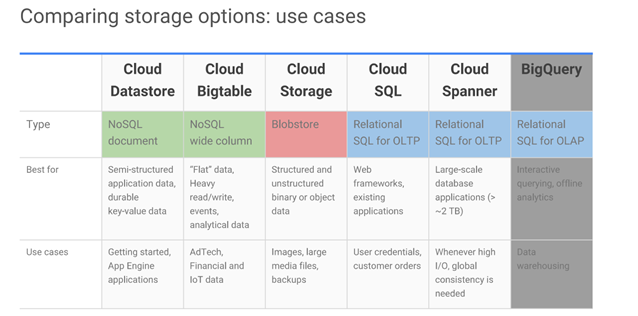
It is the summary of those storage options. We can see the type, use cases, and advantages of these options.
What is more! Google has a nice decision tree to help you determine the best option for you.
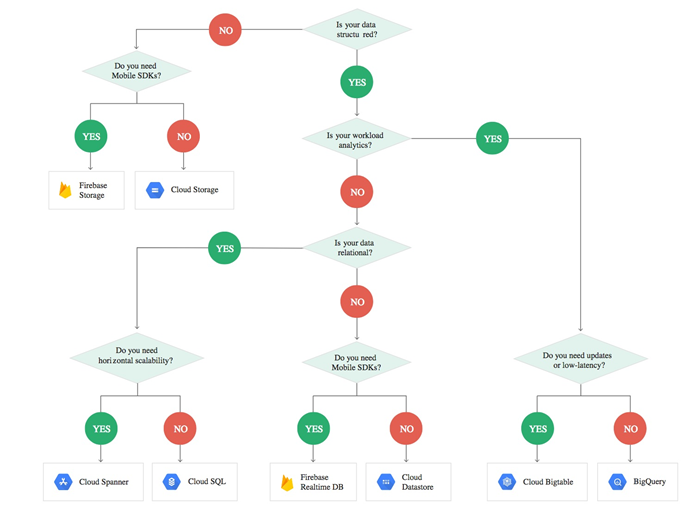
We hope the above information helps you have a better overview of the cloud storage options that google provided.