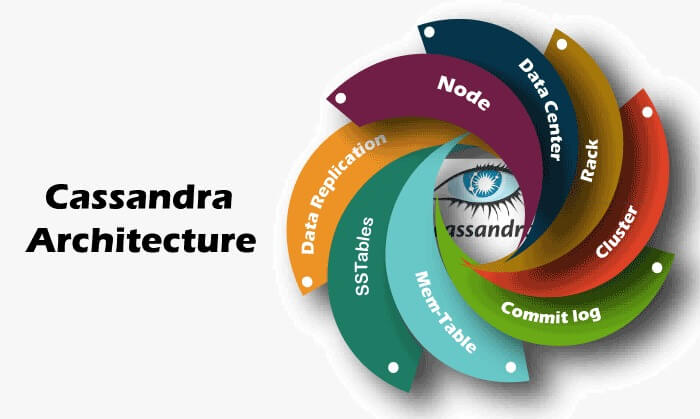
Apache Cassandra– a name synonymous with availability, reliability and scalability is a NoSQL database with a unique architecture. Let’s delve a little deeper into what the architecture of Cassandra comprises of
Cassandra clusters
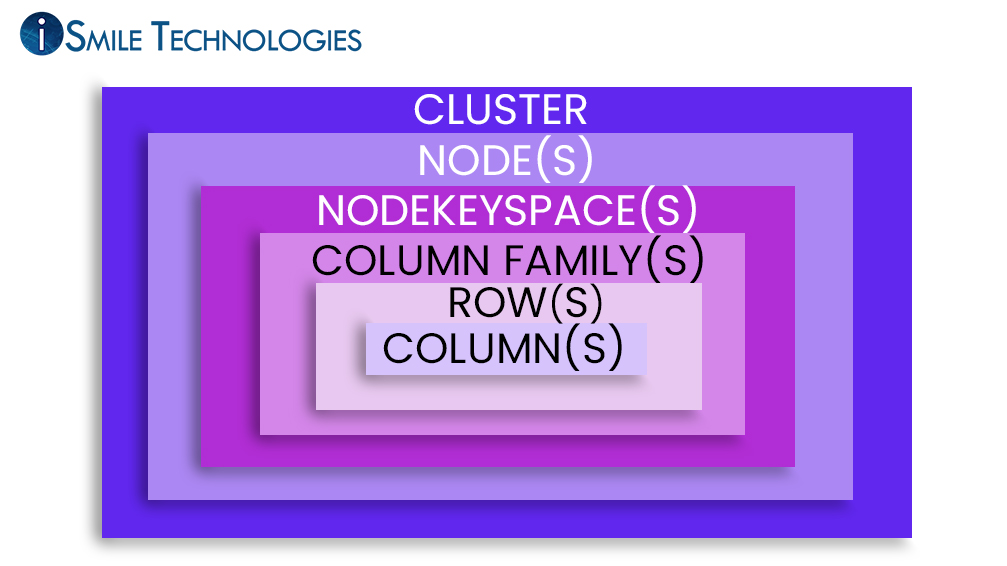
Cassandra has distributed system architecture. Each Cassandra instance (document confirming to a specific data type definition (DTD)) is called a node. You can add multiple nodes by horizontally scaling to form a cluster. A cluster is a shell in the entire Cassandra database
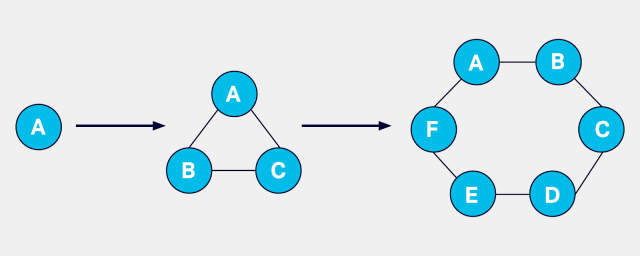
( Nodes to clusters by horizontal scaling)
Column– It is the innermost layer in the Apache Cassandra database. It is divided into different headings. The headings carry the primary data for the specific entry made
Rows– It is the next layer and are basically classifications under which the columns are divided.
Cassandra stores data in table and each table is grouped under columns and rows
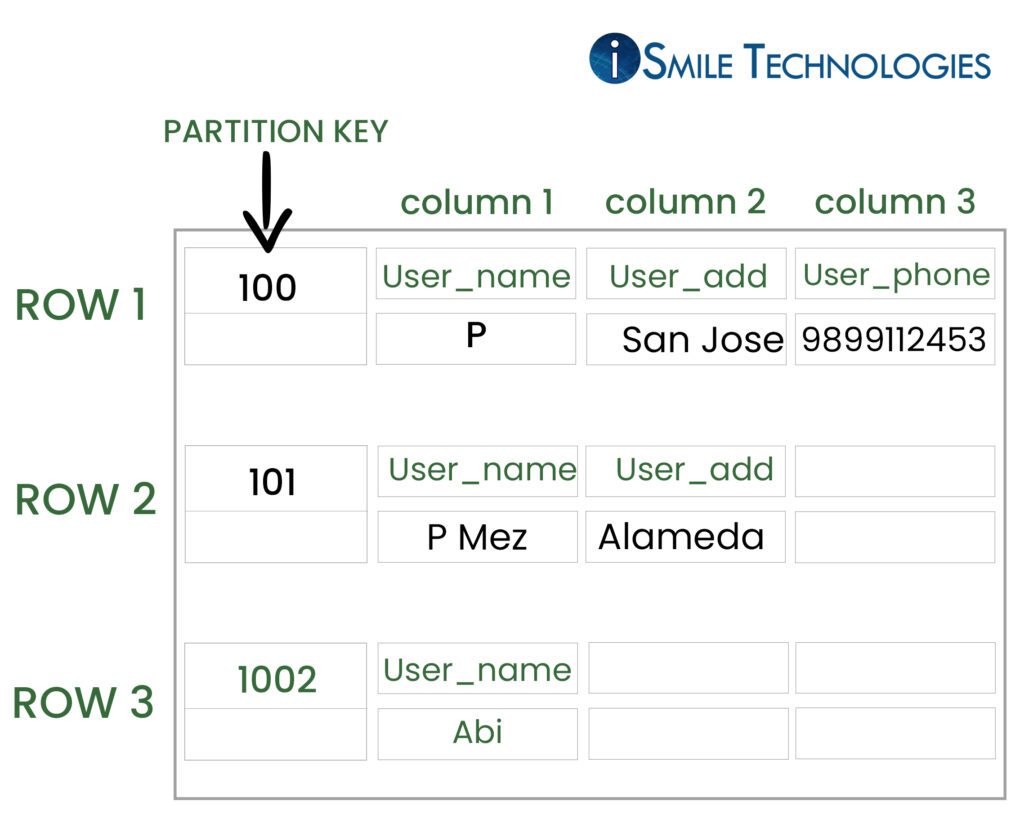
Structure of the table in Cassandra
USE User_data;
CREATE TABLE User_table (
User_id int,
User_name text,
User_add text,
User_phone text,
PRIMARY KEY (User_id)
);
Insert into User_data (User_id, User_name, User_add, User_phone )
VALUES(100, ‘P’, ‘San Jose’, ‘9899112453’);
Insert into User_data (User_id, User_name, User_add, User_phone )
VALUES(101, ‘P Maz’, ‘Alameda’);
OUTPUT
Key space– The key space is the outermost layer in the storage. It contains the main data, distributed according to their properties.
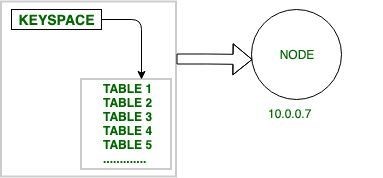
A cluster is the main entry point of the data into the Cassandra database.
Each node in Cassandra is capable of performing the entire database operations and deal with client requests individually without requiring any master node. The cluster doesn’t hold a single point of failure owing to the distributed nature of architecture.
One or more nodes in the cluster serve as replicas for the set of data. With data replication among the nodes, Cassandra ensures no single point of failure
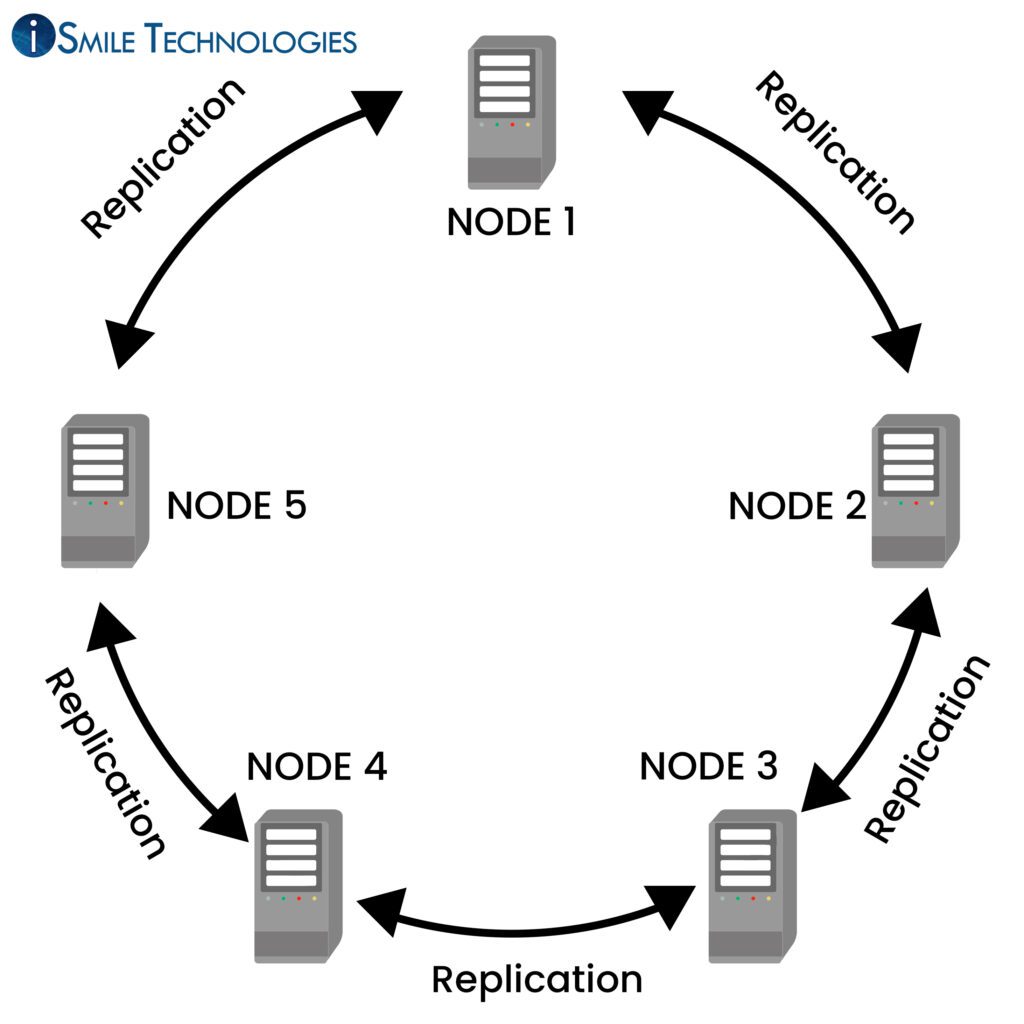
The cluster nodes communicate with each other through Gossip protocol. Gossip keeps one node apprised of the status of other nodes. Every second, one node gossips with three other nodes in the cluster.
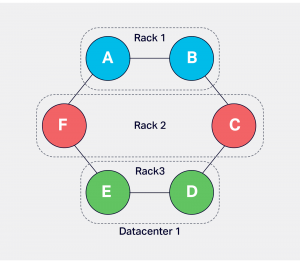
A cluster in Cassandra is divided into racks (group of metal servers collaborating resources like network switches and power source) and data centers. Snitch configuration is used to group nodes into racks and data centers. Data replication depends on the configuration of racks and data centers.
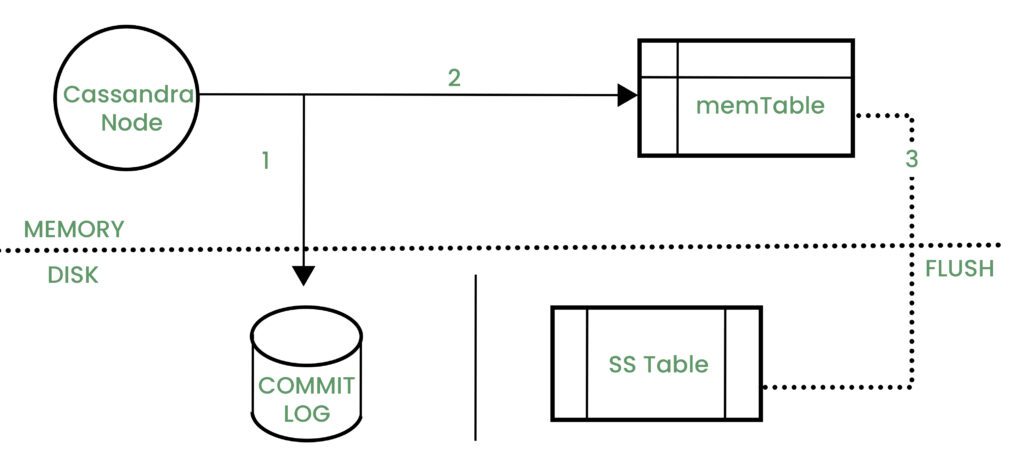
Storage in Cassandra
Commit Log- It’s the crash recovery mechanism of Cassandra or to sync issues with the server on failure of the data node. All write operations are written to commit log.
Mem-table– After commit log the data is written to the Mem-table
SS table- When the contents of the Mem-table reach a threshold value, the data is flushed from it to a disk file called the SS- table
Data Replication in Cassandra
Every data entry item in the table is replicated at M hosts where M is the configured replication factor at each instance
I hope that I have been able to outline the architecture of Apache Cassandra.
Comment or write to us.