OpenStack began in 2010 as a joint project of Rackspace Hosting and NASA. As of 2012, it was managed by the OpenStack Foundation, a non-profit corporate entity established in September 2012 to promote OpenStack software and its community. By 2018, more than 500 companies had joined the project. In 2020 the foundation announced it would be renamed the Open Infrastructure Foundation in 2021.
What is Openstack
Openstack is an Open-source Cloud Computing Platform. It is mainly deployed as infrastructure-as-a-service (IaaS) in private and public clouds. It aims to provide hardware tools and components for processing, storage, and networking resources throughout a data center.

Components of Openstack
Openstack consists of Multiple Components with a modular architecture. We are discussing brief of seven major Components as follows:
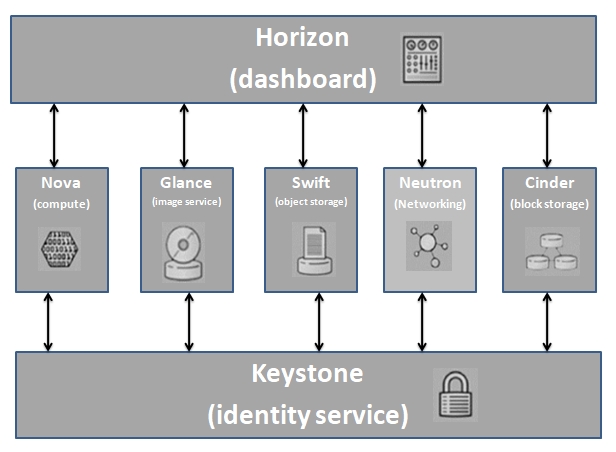
1. Horizon (dashboard):
Horizon is the canonical implementation of OpenStack’s Dashboard, providing a web-based interface for cloud administrators and tenants. It is used to manage provision and monitor cloud resources.
2. Nova (compute service):
Nova is the primary computing engine of OpenStack, responsible for instance, scheduling, creation, and termination. Nova supports many hypervisors to ensure widespread interoperability, including QEMU/KVM, XenServer, VMware ESXi, and Microsoft Hyper-V.
3. Neutron (networking service):
Neutron provides network connectivity between OpenStack instances, enabling multi-VM deployments. For this purpose, Neutron uses various software-defined networking (SDN) technologies, including Open Virtual Network (OVN), Open vSwitch (OVS), Juniper Contrail, Cisco ACI, etc.
4. Cinder (block storage):
Cinder is a storage component responsible for provisioning, managing, and terminating persistent block devices. Those can be later attached to the instances running on OpenStack to enable persistent block storage.
5. Swift (object storage):
Swift is another storage component that provides a highly available and scalable object storage service. It enables storing and retrieving unstructured data objects with the help of Restful API for both OpenStack services and instances running on the cloud.
6. Glance (image service provider):
Glance is an image service responsible for uploading, managing, and retrieving cloud images for instances running on OpenStack. Glance works across various stores to provide the most convenient location of images for organizations.
7. Keystone (identity service provider):
Keystone serves as an identity service, providing authentication and authorization functions for the users to enable multi-tenancy. Keystone can be easily integrated with external identity systems, such as lightweight directory access protocol (LDAP) or Active Directory.
Components of Openstack
Scalability:
Scalability is the primary key component of cloud computing. OpenStack offers better scalability for businesses. This feature allows enterprises to spin up and spin down servers on demand.
Security:
One of the significant features of OpenStack is security; it offers the best security feature Roll based access control (RBAC), to restrict user access as per the need.
Automation:
Compared to another option, automation is one of the primary key selling points of OpenStack. The ease with which you can automate tasks makes OpenStack efficient. The software comes with inbuilt tools that make cloud management much faster and easier.
OpenStack provides its Application Program Interface (API) that helps other applications to have complete control over the cloud. This function makes it easier to build apps that can communicate with OpenStack to perform tasks such as firing up VMs.
Fast Development:
OpenStack orchestration and self-service capabilities offer developers and IT staff faster and better access to IT resources. Because developers can provision machines rapidly and on demand, they can significantly reduce development and testing periods and have more freedom to experiment with new ideas.
Easy Access and Manage:
OpenStack is easy to access and manage because of the following features:
- Command Line Tools: We can access OpenStack using command-line tools.
- Dashboard: OpenStack offers users and administrators the means to access and manage various aspects of OpenStack using a Graphical User Interface (GUI) based dashboard component. It is available as a web UI.
- APIs: There are a lot of Application Program Interface (APIs), which is used to manage OpenStack.
Overcome the Openstack Challenges with ISmile Technologies
- ISmile Technologies provides security to Openstack’s components to prevent and manage threats.
- Deploying OpenStack is more complex than running a program and clicking the ‘next’ button until it’s finished. ISmile Technologies provides highly skilled and professional developers to overcome installation challenges.
- ISmile Technologies eases the automation process of Installing and upgrading the OpenStack software.
- ISmile Technologies provides reliability to the Openstack cloud to improve performance and speed quality.
- ISmile Technologies provides scalability to Openstack cloud to scale as you grow as per current needs and add more compute nodes to the IaaS environment as demand increases.
ISmile Technologies is a proud partner of the top public cloud providers AWS, Microsoft Azure, and Google Cloud. We can provide you with a cloud governance model, and core framework to ensure your operations in the public cloud are scalable and secure. Schedule a free assessment today.
CLOUD ENGINEER
Mahaboob Khan
A Cloud Engineer at ISmile Technologies, he had extensive experience working on Microsoft Azure which involves activities like Implementation, Managing and troubleshooting the User related issues. With automation tools like Azure ARM Template, Terraform, and Azure DevOps, he helps our client to automate deployment of IaaS and PaaS services.